►Introduction
This section of tutorial will explain you everything that you need to know about stepper motors. Stepper motors can be used in various areas of your microcontroller projects such as making robots, robotic arm, and automatic door lock System etc. This tutorial will explain you construction of stepper motors (unipolar and bipolar stepper motors ), basic principle, different controlling types (Half step and Full step), Interfacing Techniques (using L293D or ULN2003) and programming your microcontroller in C and assembly to control stepper motor.
►Bipolar stepper motor
The bipolar stepper motor usually has four wires coming out of it. Unlike unipolar steppers, bipolar steppers have no common center connection. They have two independent sets of coils instead. You can distinguish them from unipolar steppers by measuring the resistance between the wires. You should find two pairs of wires with equal resistance. If you've got the leads of your meter connected to two wires that are not connected (i.e. not attached to the same coil), you should see infinite resistance (or no continuity).
As already said, we will talk mostly on "Unipolar stepper motors" which is most common type of stepper motor available in the market.A simple example of 6 lead step motor is given below and in 5 lead step motor wire 5 and 6 are joined together to make 1 wire as common.
►Working of Stepper Motor
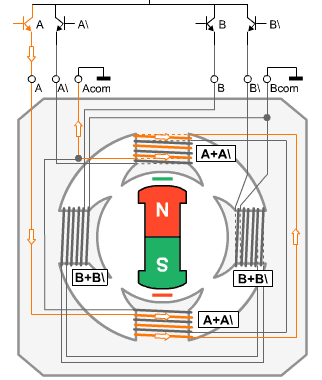
Now let’s discuss the operation Principle of a stepper motor. When we energize a coil of stepper motor, the shaft of stepper motor (which is actually a permanent magnet) align itself according to poles of energized coil. So when motor coils are energized in a particular sequence, motor shaft tend to align itself according to pole of coils and hence rotates. A small example of energizing operation is given below.

You can see in the example, when coil "A" is energized, A north-south polarity is generated at "A+A\" as shown in the figure above and magnetic shaft automatically align itself according to the poles generated. When the next coil is energized the shaft again aligns itself and takes a step. Hence the working pricipal.
We have seen that to make the stepper motor work, we need to energize coil in a sequence. The explanation and generation of the sequence is explained below.
- Full Step Sequence
- Half Step Sequence
we will go through theses equences one by one.
Full Mode Sequence
Step A B A\ B\
1 0 1 1 0
2 0 0 1 1
The working of the full mode sequence is given in the animated figure below.

Half Mode Sequence
2 0 1 1 0
3 0 0 1 0
The working of the half mode sequence is given in the animated figure below.

Step A B
0 0 1
1 1 1
2 1 0
3 0 0
►Step Sequence for Bipolar stepper motor
Step A A\ B B\
The above polarity sequence can be interpreted in terms of logic levels for microcontroller by activating one coil at a time as shown in the table below.
Step A A\ B B\
0 1 0 0 0
1 0 0 1 0
2 0 1 0 0
3 0 0 0 1
We have now learnt most of the necessary things regarding a stepper motor. In the next section we will discuss about the various techniques to interface a stepper motor.
►Connecting Unipolar Stepper Motor
- Interface using L293D - H-Bridge Motor Driver
- Interface using ULN2003/2004 - Darlington Arrays
We will dicuss both connection techniques one by one. The above mentioned methods need 4 controller pins for interface.
►Connecting Unipolar stepper using L293D

As you see in the circuit above the four pins "Controller pin 1",2,3 and 4 will control the motion and direction of the stepper motor according to the step sequence programmed in the controller.
►Connecting Unipolar stepper using ULN2003/2004
 As already discussed in case of L293D, Here in this circuit too the four pins "Controller pin 1",2,3 and 4 will control the motion and direction of the stepper motor according to the step sequence sent by the controller.
As already discussed in case of L293D, Here in this circuit too the four pins "Controller pin 1",2,3 and 4 will control the motion and direction of the stepper motor according to the step sequence sent by the controller.
►2-wire connection for Unipolar Stepper Motor
We have seen the generally used 4-wire connection method for interfacing unipolar stepper motor, but we can simplify the design to make controller use less pins with the help of 2-wire connection method. The circuit for 2-wire connection is shown below.

►Connecting Bipolar Stepper Motors
we have studied that, Bi-polar stepper motors has 2 different coils. The step sequence for bipolar stepper motor is same as that of unipolar stepper motors. The driving circuits for this require an H-Bridge as it allows the polarity of the power applied to be controlled independently. This can be done as shown in the figure below:

Now we have seen the methods for connecting stepper motors with your microcontroller. So keeping these circuits in mind, we will now look at the programming of microcontroller to control stepper motors. This is discussed in the next section of the tutorial.
►Programming Full step Sequence
►C Programming
I am assuming that stepper motor is connected at Port 1.0 to Port 1.3. Adjusting the delay will increase or decrease the speed of the motor. Here just for demonstration i have taken some delay, you can change it as you want.
CODE:
#include
void delay()
{
unsigned char i,j,k;
for(i=0;i<6;i++)>
for(j=0;j<255;j++)>
for(k=0;k<255;k++);
}
►Assembly Programming
CODE:
org 0H
stepper equ P1
main:
mov stepper, #0CH
acall delay
mov stepper, #06H
acall delay
mov stepper, #03H
acall delay
mov stepper, #09H
acall delay
sjmp main
delay:
mov r7,#4
wait2:
mov r6,#0FFH
wait1:
mov r5,#0FFH
wait:
djnz r5,wait
djnz r6,wait1
djnz r7,wait2
ret
end
The working of the above code can be seen in the demo animation below.

while(1)
stepper = 0x08;
delay();
stepper = 0x0C;
delay();
stepper = 0x04;
delay();
stepper = 0x06;
delay();
stepper = 0x02;
delay();
stepper = 0x03;
delay();
stepper = 0x01;
delay();
stepper = 0x09;
delay();
}
}
►Assembly Programming
CODE:
mov stepper, #08H
acall delay
mov stepper, #0CH
acall delay
mov stepper, #04H
acall delay
mov stepper, #06H
acall delay
mov stepper, #02H
acall delay
mov stepper, #03H
acall delay
mov stepper, #01H
acall delay
mov stepper, #09H
acall delay
sjmp main
The working of the above code can be seen in the demo animation below.

►Programming for 2-wire connection of Unipolar Stepper Motor
►C Programming
while(1)
delay();
stepper = 0x01;
delay();
stepper = 0x00;
delay();
stepper = 0x02;
delay();
}
}
►Assembly Programming
mov stepper, #03H
acall delay
mov stepper, #01H
acall delay
mov stepper, #00H
acall delay
mov stepper, #02H
acall delay
sjmp main
The working of the above code can be seen in the demo animation below.

►C Programming
CODE:
while(1)
stepper = 0x08;
delay();
stepper = 0x02;
delay();
stepper = 0x04;
delay();
stepper = 0x01;
delay();
}
}
mov stepper, #08H
acall delay
mov stepper, #02H
acall delay
mov stepper, #04H
acall delay
mov stepper, #01H
acall delay
sjmp main




